COEN 146代写、代做TCP/IP Socket Programming
COEN 146: Computer Networks
Lab 3: TCP/IP Socket Programming
Objectives
1.To develop client/ server applications using TCP/IP Sockets
2.To write a C program to transfer file over TCP/IP Socket
TCP/IP Client/ Server[ http://beej.us/guide/bgnet/]
The following figure shows the steps taken by each program:
On the client and server sides:
The socket() system call creates an unbound socket in a communications domain, and return a file descriptor that can be used in later function calls that operate on sockets.
int sockfd = socket(domain, type, protocol)
●sockfd: socket descriptor, an integer (like a file-handle)
●domain: integer, communication domain e.g., AF_INET (IPv4 protocol) , AF_INET6 (IPv6 protocol), AF_UNIX (local channel, similar to pipes)
●type: communication type
SOCK_STREAM: TCP (reliable, connection oriented)
SOCK_DGRAM: UDP (unreliable, connectionless)
SOCK_RAW (direct IP service)
●protocol: This is useful in cases where some families may have more than one protocol to support a given type of service. Protocol value for Internet Protocol (IP), which is 0. This is the same number which appears on protocol field in the IP header of a packet.
#include <sys/socket.h>
...
...if ((server_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) < 0)
{
perror(“cannot create socket”);
return 0;
}
On the server side:
After creation of the socket, bind() system call binds the socket to the address and port number specified in addr(custom data structure). In the example code, we bind the server to the localhost, hence we use INADDR_ANY to specify the IP address.
int bind (int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
●addr: Points to a sockaddr structure containing the address to be bound to the socket. The length and format of the address depend on the address family of the socket.
●addrlen: Specifies the length of the sockaddr structure pointed to by the addr argument.
The listen() function puts the server socket in a passive mode, where it waits for the client to approach the server to make a connection.
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
●backlog: defines the maximum length to which the queue of pending connections for sockfd may grow. If a connection request arrives when the queue is full, the client may receive an error with an indication of ECONNREFUSED.
The accept() system call extracts the first connection request on the queue of pending connections for the listening socket (sockfd), creates a new connected socket, and returns a new file descriptor referring to that socket. At this point, connection is established between client and server, and they are ready to transfer data.
int new_socket= accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
On the client side:
The connect() system call connects the socket referred to by the file descriptor sockfd to the address specified by addr. Server’s address and port is specified in addr.
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
Read and write over socket:
bzero(buffer, 256);
n = read(newsockfd, buffer, 255);
if (n < 0) error("ERROR reading from socket");
printf("Here is the message: %s
", buffer);
This code initializes the buffer using the bzero() function, and then reads from the socket.
Note that the read call uses the new file descriptor, the one returned by accept(), not the original file descriptor returned by socket().
Note also that the read() will block until there is something for it to read in the socket, i.e. after the client has executed a write(). It will read either the total number of characters in the socket or 255, whichever is less, and return the number of characters read
n = write(newsockfd, "I got your message", 18);
if (n < 0) error("ERROR writing to socket");
Once a connection has been established, both ends can both read and write to the connection. Naturally, everything written by the client will be read by the server, and everything written by the server will be read by the client. This code simply writes a short message to the client. The last argument of write is the size of the message.
Structures:
Address format
An IP socket address is defined as a combination of an IP interface address and a 16-bit port number. The basic IP protocol does not supply port numbers, they are implemented by higher level protocols like UDP and TCP. On raw sockets sin_port is set to the IP protocol.
struct sockaddr_in {
sa_family_t sin_family; /* address family: AF_INET */
in_port_t sin_port; /* port in network byte order */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* internet address */
};
/* Internet address. */
struct in_addr {
uint32_t s_addr; /* address in network byte order */
};
This is defined in netinet/in.h
sin_family is always set to AF_INET.
sin_port contains the port in network byte order. The port numbers below 1024 are called privileged ports (or sometimes: reserved ports). Only privileged processes) may bind to these sockets.
sin_addr is the IP host address.
s_addr member of struct in_addr contains the host interface address in network byte order.
in_addr should be assigned one of the INADDR_* values (e.g., INADDR_ANY) or set using the inet_aton, inet_addr, inet_makeaddr library functions or directly with the name resolver (see gethostbyname).
INADDR_ANY allows your program to work without knowing the IP address of the machine it was running on, or, in the case of a machine with multiple network interfaces, it allowed your server to receive packets destined to any of the interfaces.
INADDR_ANY has the following semantics: When receiving, a socket bound to this address receives packets from all interfaces. For example, suppose that a host has interfaces 0, 1 and 2. If a UDP socket on this host is bound using INADDR_ANY and udp port 8000, then the socket will receive all packets for port 8000 that arrive on interfaces 0, 1, or 2. If a second socket attempts to Bind to port 8000 on interface 1, the Bind will fail since the first socket already “owns” that port/interface.
Example:
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl (INADDR_ANY);
●Note: "Network byte order" always means big endian. "Host byte order" depends on architecture of host. Depending on CPU, host byte order may be little endian, big endian or something else.
●The htonl() function translates a long integer from host byte order to network byte order.
To bind socket with localhost, before you invoke the bind function, sin_addr.s_addr field of the sockaddr_in structure should be set properly. The proper value can be obtained either by
my_sockaddress.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1")
or by
my_sockaddress.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_LOOPBACK);
To convert an address in its standard text format into its numeric binary form use the inet_pton() function. The argument af specifies the family of the address.
#define _OPEN_SYS_SOCK_IPV6
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int inet_pton(int af, const char *src, void *dst);
Recap - File transfer:
●Binary file: jpg, png, bmp, tiff etc.
●Text file: txt, html, xml, css, json etc.
You may use functions or system calls for file transfer. C Function connects the C code to file using I/O stream, while system call connects C code to file using file descriptor.
●File descriptor is integer that uniquely identifies an open file of the process.
●I/O stream sequence of bytes of data.
A Stream provides high level interface, while File descriptor provide a low-level interface. Streams are represented as FILE * object, while File descriptors are represented as objects of type int.
C Functions to open and close a binary/text file
fopen(): C Functions to open a binary/text file, defined as:
FILE *fopen(const char *file_name, const char *mode_of_operation);
where:
●file_name: file to open
●mode_of_operation: refers to the mode of the file access, For example:- r: read , w: write , a: append etc
●fopen() return a pointer to FILE if success, else NULL is returned
●fclose(): C Functions to close a binary/text file.
fclose(): C Functions to close a binary/text file, defined as:
fclose( FILE *file_name);
Where:
●file_name: file to close
●fclose () function returns zero on success, or EOF if there is an error
C Functions to read and write a binary file
fread(): C function to read binary file, defined as:
fread(void * ptr, size_t size, size_t count, FILE * stream);
where:
●ptr- it specifies the pointer to the block of memory with a size of at least (size*count) bytes to store the objects.
●size - it specifies the size of each objects in bytes.
●count: it specifies the number of elements, each one with a size of size bytes.
●stream - This is the pointer to a FILE object that specifies an input stream.
●Returns the number of items read
fwrite (): C function to write binary file, defined as:
fwrite (void *ptr, size_t size, size_t count, FILE *stream);
where:
●Returns number of items written
●*arguments of fwrite are similar to fread. Only difference is of read and write.
For example:
To open "lab3.dat" file in read mode then function would be:
FILE* demo; // demo is a pointer of type FILE
char buffer[100]; // block of memory (ptr)
demo= fopen("lab3.dat", "r"); // open lab3.dat in read mode
fread(&buffer, sizeof(buffer), 1, demo); // read 1 element of size = size of buffer (100)
fclose(demo); // close the file
C Functions to read and write the text file.
fscanf (): C function to read text file.
fscanf(FILE *ptr, const char *format, ...)
Where:
●Reads formatted input from the stream.
●Ptr: File from which data is read.
●format: format of data read.
●returns the number of input items successfully matched and assigned, zero if failure
fprintf(): C function to write a text file.
fprintf(FILE *ptr, const char *format, ...);
Where:
●*arguments similar to fscanf ()
For example:
FILE *demo; // demo is a pointer of type FILE
demo= FILE *fopen("lab3.dat", "r"); // open lab3.dat in read mode
/* Assuming that lab3.dat has content in below format
City
Population
….
*/
char buf[100]; // block of memory
fscanf(demo, "%s", buf); // to read a text file
fclose(demo); // close the file
*to read whole file use while loop
System Call to open, close, read and write a text/binary file.
open(): System call to open a binary/text file, defined as:
open (const char* Path, int flags [, int mode ]);
Where:
●returns file descriptor used on success and -1 upon failure
●Path :- path to file
●flags :- O_RDONLY: read only, O_WRONLY: write only, O_RDWR: read and write, O_CREAT: create file if it doesn’t exist, O_EXCL: prevent creation if it already exists
close(): System call to close a binary/text file, defined as:
close(int fd);
where:
●return 0 on success and -1 on error.
●fd : file descriptor which uniquely identifies an open file of the process
read(): System call to read a binary/text file.
read (int fd, void* buf, size_t len);
where:
●returns 0 on reaching end of file, -1 on error or on signal interrupt
●fd: file descriptor
●buf: buffer to read data from
●len: length of buffer
write(): System call to write a binary/text file.
write (int fd, void* buf, size_t len);
where:
●*arguments and return of write are similar to read().
For example:
int fd = open("lab3.dat", O_RDONLY | O_CREAT); //if file not in directory, file is
created
Close(fd);
Implementation steps:
Step 1.[30%] Write a C program for a TCP server that accepts a client connection for file transfer.
Step 2.[25%] Write a C program for a TCP client that connects to the server. In this case
a.The client connects to the server and request a file to download from the server.
b.The server accepts the connection and transfers the file to the client
Step 3.Compile and run. Note: you may use the IP address 127.0.0.1 (loop back IP address) for a local host, i.e. both of your client and server run on the same machine.
[20%] Demonstrate your program to the TA:
a.Your client and server on your same machine
b.Your client and your classmate’s server IP address. You may to discuss with the TA if you run into access problems
Multiple Clients – Concurrent Server
In general, a TCP server is designed as a concurrent server to server multiple clients. This means when a client sends a request for a file transfer, the sever accepts the connection request and spawns a thread to handle this transfer on the connection descriptor. The server will then continue in a loop listening for another client connection request to handle another file transfer.
Step 4.[20%] Write a C program for a concurrent TCP server that accepts and responds to multiple client connection requests, each requesting a file transfer. Modify your TCP server in Step 1 so that when the server accepts a connection from a client it spawns a separate thread to handle this specific client connection for file transfer.
Note: You will have several threads (at the same time) running on the server transferring copies of src.dat files to clients that each will save at their destination as – dst.dat file (possibly needs to be numbered differently on the same host).
[5%] Demonstrate to the TA, multiple clients making file transfer request to the server and that the server makes multiple transfers at the same time. Make N = 5. Upload your source code to Camino.
Note: To be able to see 5 threads handling connections at the same time, you may need to introduce a delay of a few second in the process of data transfer to make it visible. This is due to the fact completing thread file transfer takes a fraction of a millisecond if not a microsecond.
Requirements to complete the lab
1.Demo to the TA correct execution of your programs [recall: a successful demo is 25% of the grade]
2.Submit the source code of your program as .c files on Camino
Please start each program with a descriptive block that includes minimally the following information:
请加QQ:99515681 邮箱:99515681@qq.com WX:codinghelp
- CHINC2024丨神州医疗重磅发布大模型及一体机,引领医疗AI行业高质量发展
- 外贸小白迷茫中 WhatsApp拉群营销工具有什么好用的 值得推荐吗
- 初出茅庐的喜悦 她通过WhatsApp拉群工具实现了全球品牌的极速传播 覆盖面达到了95%
- Ins一键群发工具,Instagram群发群控工具,让你的营销更高效!
- Instagram营销引流新趋势,Ins智能群发采集软件最新上线!
- CS202代做、代写Java/Python程序语言
- 神经外科医疗器械白皮书(2023版)正式上线!
- WhatsApp/ws群发/ws协议号/ws频道号出售
- Vision Pro有了,谁是空间计算时代的“安卓机皇”?
- CSC3150代写、Java/C++程序语言代做
- ws/WhatsApp群发如何避免封控,ws最靠谱的协议号
- WhatsApp拉群之谜 外贸小白为何对这个营销工具心生好奇
- WhatsApp拉群营销工具改变我的命运,营业额飙升到新高度
- 科普:USB的诞生发展史 以及未来USB发展方向
- 电报群发引流秘籍,Telegram批量采集隐藏用户/TG群发软件
- 半岛超声炮团队重磅上新! 医疗器械大厂重构居家美容新方式!
- 东方甄选又用一份不太理想的中报,给了投资者一顿暴击
- 倍效果 1个工具 WhatsApp拉群营销 数字化魔法的起点
- 跨境推广新选择!Telegram群发云控带您挖掘海外市场的无限商机
- 未知星球的秘密 科技魔法如何通过WhatsApp拉群工具为我带来业务的不可思议变革
- Instagram营销软件,ins群发引流工具/ig拉群/ins业务咨询大轩
- WhatsApp拉群营销 新法宝
- 外贸新手必学WtApp工具轻松掌握市场动向事业腾飞
- Ins/IG自动吸客软件攻略:Instagram精准私信群发助手教你如何实现!
- 数字营销中的目标受众WhatsApp筛选器-WhatsApp营销工具是我业务成功的启动器!
- 代做ELEC 292、代写Python/c++编程设计
- 引领智能制造新方向 | 谷器数据MES荣获北京市新技术新产品(服务)证书
- AI服务器滑轨供应商南俊国际转盈
- 数字奇兵:科技魔法师驾驭WhatsApp拉群,点燃市场风暴
- Instagram营销软件,ins群发工具,ig引流软件/测试联系大轩
推荐
-
 如何经营一家好企业,需要具备什么要素特点
我们大多数人刚开始创办一家企业都遇到经营
科技
如何经营一家好企业,需要具备什么要素特点
我们大多数人刚开始创办一家企业都遇到经营
科技
-
 全力打造中国“创业之都”名片,第十届中国创业者大会将在郑州召开
北京创业科创科技中心主办的第十届中国创业
科技
全力打造中国“创业之都”名片,第十届中国创业者大会将在郑州召开
北京创业科创科技中心主办的第十届中国创业
科技
-
 升级的脉脉,正在以招聘业务铺开商业化版图
长久以来,求职信息流不对称、单向的信息传递
科技
升级的脉脉,正在以招聘业务铺开商业化版图
长久以来,求职信息流不对称、单向的信息传递
科技
-
 疫情期间 这个品牌实现了疯狂扩张
记得第一次喝瑞幸,还是2017年底去北京出差的
科技
疫情期间 这个品牌实现了疯狂扩张
记得第一次喝瑞幸,还是2017年底去北京出差的
科技
-
 创意驱动增长,Adobe护城河够深吗?
Adobe通过其Creative Cloud订阅捆绑包具有
科技
创意驱动增长,Adobe护城河够深吗?
Adobe通过其Creative Cloud订阅捆绑包具有
科技
-
 智慧驱动 共创未来| 东芝硬盘创新数据存储技术
为期三天的第五届中国(昆明)南亚社会公共安
科技
智慧驱动 共创未来| 东芝硬盘创新数据存储技术
为期三天的第五届中国(昆明)南亚社会公共安
科技
-
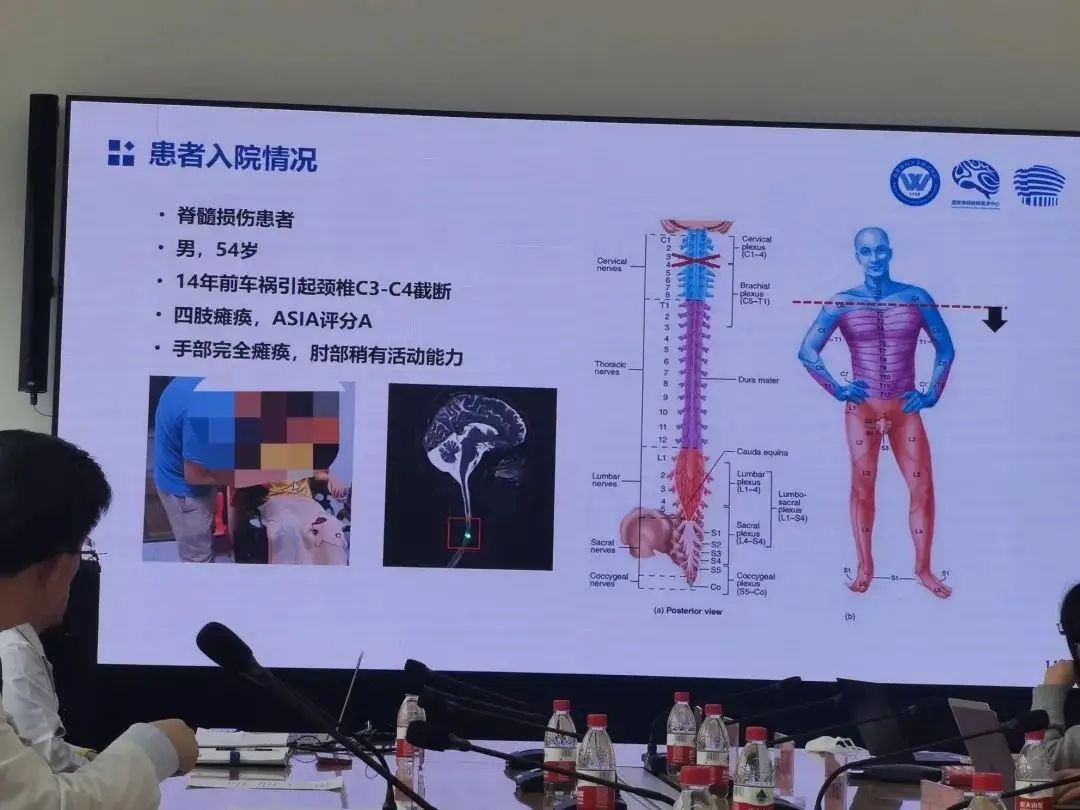 老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他由此产生了新的憧憬
瘫痪十四年后,老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他
科技
老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他由此产生了新的憧憬
瘫痪十四年后,老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他
科技
-
 B站更新决策机构名单:共有 29 名掌权管理者,包括陈睿、徐逸、李旎、樊欣等人
1 月 15 日消息,据界面新闻,B站上周发布内部
科技
B站更新决策机构名单:共有 29 名掌权管理者,包括陈睿、徐逸、李旎、樊欣等人
1 月 15 日消息,据界面新闻,B站上周发布内部
科技
-
 丰田章男称未来依然需要内燃机 已经启动电动机新项目
尽管电动车在全球范围内持续崛起,但丰田章男
科技
丰田章男称未来依然需要内燃机 已经启动电动机新项目
尽管电动车在全球范围内持续崛起,但丰田章男
科技
-
 苹果罕见大降价,华为的压力给到了?
1、苹果官网罕见大降价冲上热搜。原因是苹
科技
苹果罕见大降价,华为的压力给到了?
1、苹果官网罕见大降价冲上热搜。原因是苹
科技

