Computer Lab 代做、代写C++编程语言
Computer Lab Assignment #3, S1 2024
Date Issued: see Wattle page
Due Date: see Wattle page
Weighting: 12
Instruction:
All homework assignments must be completed individually. We encourage you to discuss the
assignments with other students. However, you should not share any of your codes with anyone
else. Each student is responsible for implementing the assignment on their own. You may assist
other in debugging their codes, but you should not copy and paste. ANU is using TurnItIn to
detect possible duplications. Consulting with previous year students who enrolled in this course
on specific assignment is also not allowed. You may use the internet as a resource for learning the
materials, but you should not borrow any existing codes found online.
The homework assignments involve a significant amount of C++ programming. However, for most
cases, a skeletal code base is provided, and you only need to fill in the missing parts, and/or fix
bugs if any.
You will submit a single ZIP file as your submission, which must contain the following files:
(1) All source codes (ending in .h, or .hpp, or .cpp), and your Makefile, CMakeLists.txt. Please
include all needed source codes for successful compilation. Please also remove all intermediate
files (such as ./vs. ./build. ) that are not needed for the compilation – Failing to do so will
lead to penalty to the marks.
(2) A written CLab3 Lab Report (minimum 10-point font size, single column, in PDF format,
with task statement, methods used, any new features that you have implemented, any known
bugs in your code, answer any questions that have been asked in the task, instruction for
the tutor to use your code, example experiment results. )
Your ZIP file must be named as “COMPX610 2024 HW3 UID.zip”. Replace ‘X’ with 4 or 8.
Replace the UID with your Uxxxxxxxx; Please submit your ZIP file to Wattle before the deadline.
Late submission will lead to penalty as per the ANU policy. Later-than-one-week submission will
1
not be accepted, which may result zero mark, unless a pre-approval for special consideration is
obtained in written before the submission deadline.
In C-Lab-3, you will be practising how to efficiently process 3D meshes. Specifically, there are
two tasks to complete: T1: half-edge data structure, and T2: mesh simplification. We
provide the general code framework for completing these two tasks and it is highly recommended
to use it. However, you’re also welcomed to build up your own pipeline as long as it satisfy all the
requirements.
Task-1: half-edge data structure
In this task, you will build upon your knowledge of C++ and graphics by creating a half-edge
data structure from interlinked pointers, and then compute important geometry and topology
properties, and visualize your mesh using MeshLab or Blender.
Steps to take:
(1) Use the two OBJ meshes provided in ”model” folder (bigguy2.obj, teeth.obj) to conduct the
following experiments and report their results. You are also welcomed to download other
complex 3D meshes in OBJ file format from the internet to test your algorithms. Make sure
that each of the meshes satisfies the following properties:
• The mesh contains a single connected component.
• The mesh must be watertight, i.e., a valid manifold surface that encloses a volume.
(2) Complete the following implementations in task1.cpp:
• Load the mesh in OBJ file format and represent the loaded mesh in the memory
by a half-edge data structure. In this step, you’ll need to implement the function
Mesh::convert obj format to mesh();
• Iterate all half edges that points away from given vertex by implementing the function
Vertex::neighbor half edges();
• Iterate all member vertices of given face by implementing Face::vertices().
• Compute its topology properties (genus number). You’ll have to implement the function
Mesh::compute genus();
• Compute its volume by implementing Mesh::compute volume();
• Compute its surface areas by implementing Mesh::compute surface area()
• Compute the average degree of all the vertices by implementing
Mesh::compute average degree().
(3) Your lab report should contain the following contents:
2
• Put the screenshot of the mesh represented by half-edge data structure
• Brief introduction describing the process of your conversion (a pseudo-code will be best
for clarification)
• Show the geometric properties (e.g. number of vertices, faces, half-edges and edges) of
the mesh as well as your topology computation results with the screenshot from the
terminal output.
Hint:
Half-edge data structure consists of four basic components: Vertex, Face, HalfEdge, and
Edge. The format of the half-edge data structure is outlined below, and basic class member
variables are already provided in include/mesh components.hpp. (Additional member
variables and member functions are used in task2, you can ignore it for now.)
Reference guide:
https://cs418.cs.illinois.edu/website/text/halfedge.html
https://cs184.eecs.berkeley.edu/sp24/docs/half-edge-intro
The Vertex class contains variables for the following information:
• A Vector3 for storing its (x, y, z) position;
• A pointer to one of the HalfEdges that points away from this Vertex;
• A unique integer identifier for the Vertex.
The Face class contains variables for the following information:
• A pointer to one of the HalfEdges that lies on this Face;
• A unique integer identifier for the Face.
The HalfEdge class contains variables for the following information:
• A pointer to the next HalfEdge in the loop of HalfEdges that lie on this HalfEdge’s Face;
• A pointer to the HalfEdge that lies parallel to this HalfEdge and which travels in the
opposite direction and is part of an adjacent Face, i.e., this HalfEdge’s symmetrical
HalfEdge;
• A pointer to the Edge on which this HalfEdge represents;
• A pointer to the Face on which this HalfEdge lies;
• A pointer to the Vertex that this HalfEdge originates from;
• A unique integer identifier for the HalfEdge.
The Edge class contains variables for the following information:
• A pointer to one of the HalfEdges that represents this Edge;
• A unique integer identifier for the Edge.
In your Lab report, you should clearly visualise the mesh, and list key results to demonstrate your
solutions.
3
Task-2: Simplify the mesh using quadratic error metrics
Purpose:
The goal of this task is to load a mesh and to simplify the mesh down to a specified number
of triangles. You will learn about modern mesh simplification algorithms with a half-edge data
structure.
Description:
In this task, we will perform mesh simplification algorithm based on quadric error metric (QEM),
you may read the following paper for reference:
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/˜
./garland/Papers/quadrics.pdf
To perform surface simplification, you should use the half-edge data structure implemented in
task1 to achieve a pair-contraction operator for the mesh. This pair-contraction operation should
preserve the topology of the surface.
To reduce the difficulty of the implementation, we’ll simplify the algorithm in the original paper
introduced as follows:
4
(1) When choosing valid pairs (v1, v2) and perform contraction, we only consider cases where
(v1, v2) form an edge. Without loss of generality, we’ll use the term “pair contraction” and
“edge collapse” interchangeably.
(2) We will not use the point-to-plane distance as discussed in the paper that computes the
distance to adjacent planes to act as error metric, because degenerate cases may make the
problem more difficult to solve. Instead, we will use distance to adjacent vertices with the
derivation below. You should collapse edges in the order dictated by the error function below
and place new vertices at the minimizer of this error function:
• Let E(v) = Pn
i=1(v − vi)
2 be the error function associated with each vertex v of the
mesh, where {vi
, i = 1. . . n} are the neighbours of v. If we expand this quadratic,
we find that E(v) = nvT
v − 2v
T Pn
i=1 vi +
Pn
i=1 v
T
i
vi
, whose minimizer is given by
v =
Pn
i=1 vi/n.
• We can further rewrite E(v) as vector dot product form, which is: E(v) =
n
Pn
i=1 vi
Pn
i=1 v
T
i
vi
T
v
T
v −2v 1
. Therefore, all we need to store to represent
this quadratic is the coefficient q =
n
Pn
i=1 vi
Pn
i=1 v
T
i
vi
, which is a 5-d vector.
• The benefit of this representation is that when creating the combined quadratic for
the union of two vertices, we simply need to sum the two vectors, each containing 5
numbers, together for the two different vertices.
You should perform edge-collapse operations using the error function above until you achieve the
desired number of polygons or there are no more edges that can be collapsed safely. The processing
time must be below one minutes. Your report should display the original and simplified surface
and also report the number of vertices, faces and edges respectively.
You must disallow edge collapses if they create illegal topology. While you should work
independently, it is a good idea to compare your results with other students, to verify code
correctness. You should assure in your input OBJ all the polygons are triangles and
the input surface is closed.
Steps to take:
Perform mesh simplification in task2.cpp. We already provide the code framework for this
function and all you need to do is to complete the missing functions as specified in the code.
However, you’re also welcomed to implement the whole pipeline in your own way as long as it
successfully achieves the simplification functionality and generate the same results. Complete the
following functionalities:
(1) Vertex::compute qem coeff() to compute the coefficient vector q that represent the
quadratic coefficient of this vertex.
(2) Edge::compute contraction() to compute the following results for this edge (v1, v2),
which will be used later to perform edge collapse:
• The optimal contraction target v
∗
;
5
• The quadratic error metrics E(v
∗
) which is the combined quadratic for the union of
v1, v2. Note that the computed results will become the cost of contracting this edge.
(3) Edge::edge contraction() to perform edge-collapse, which we will write as (v1, v2) →
v
∗
. It contains the following steps:
• Moves the vertex v1 to the new position v*, remember to update all corresponding
attributes
• Connects all incident edges of v1 and v2 to v*, and remove the vertex v2
• Any faces, half edges, and edges associated with this collapsed edge will be removed.
(4) Your lab report should contain the following contents:
• Use the two OBJ meshes provided in ”model” folder to demonstrate the results.
• Display the original mesh as well as the simplified mesh with MeshLab or Blender.
• Take the screenshot of the mesh geometric information as well as the verification results
from the terminal output to demonstrate the correctness of your implementation.
More example mesh surfaces can be found here: happy, teddy
Your ZIP file must be named as "COMPX610 2024 HW3 UID.zip".
== END OF CLAB-3 ==
请加QQ:99515681 邮箱:99515681@qq.com WX:codinghelp
- Telegram批量私信工具,TG一键群发私信助手,电报群发私信软件
- 商家智能推广首选,个性服务不容错过!ins群发协议,品牌建设利器!
- Telegram群发云控征途的科技明星:全球app云筛帮你精确锁定海外市场的核心受众
- 电报最强群发助手推荐,Telegram群发工具,TG群发拉群助手
- 办公减碳3000吨!远东电缆携手法大大电子合同,响应绿色办公
- 丰田章男称未来依然需要内燃机 已经启动电动机新项目
- 中国节能灯:照亮未来,点亮绿色生活
- CPT408代写、代做Java,Python程序
- 南京威雅学校:创校生特辑——小小少年,博物天下
- Computer Lab 代做、代写C++编程语言
- 外贸初探 WhatsApp拉群营销工具是我事业起飞的秘密武器
- 数字迷境大揭秘:科技魔法师的Telegram协议号营销工具,引发好奇的科技探秘
- Instagram营销引流软件,ins群发助手/ig拉群神器推荐/测试咨询大轩
- 数字化引爆,转化率狂飙 WhatsApp拉群工具 数字营销的巅峰之选
- 首个管家服务白皮书发布 万科物业重新定义物业服务
- 中国品牌崛起,爱可声助听器在欧美市场崭露头角
- 欧美用户真实反馈!他们为什么选择爱可声助听器?
- Telegram营销软件如何主宰群发筛选引流市场
- Telegram/TG群发拉群自动化软件,电报/TG精准营销软件,TG/纸飞机全自动注册
- household energy consumption编程代做
- Instagram营销软件 - ins群发工具/ig营销助手/ins引流神器
- 2024“一带一路”瓜菜产业发展大会在新疆疏勒盛大开幕
- 6 Force-Directed digram代写、代做 java/Python 编程
- 国家重点研发计划“主动健康”专项课题终期验收会召开,神州医疗承担课题顺利通过验收
- Temu和Shein在Meta投了多少钱
- WhatsApp拉群营销利器 有人发现了吗 分享一下你的独特体验
- 新迪数字2024新品发布会即将盛大启幕,亮点先睹为快!
- Instagram营销软件 - ins采集软件/ig采集助手/ins群发助手
- Telegram引流群发营销软件引快速扩客方式推荐
- 全球营销星际商务奇谭:Line群发云控工具是科技魔法的催化剂,引领我进入业务的星际时代
推荐
-
 疫情期间 这个品牌实现了疯狂扩张
记得第一次喝瑞幸,还是2017年底去北京出差的
科技
疫情期间 这个品牌实现了疯狂扩张
记得第一次喝瑞幸,还是2017年底去北京出差的
科技
-
 升级的脉脉,正在以招聘业务铺开商业化版图
长久以来,求职信息流不对称、单向的信息传递
科技
升级的脉脉,正在以招聘业务铺开商业化版图
长久以来,求职信息流不对称、单向的信息传递
科技
-
 创意驱动增长,Adobe护城河够深吗?
Adobe通过其Creative Cloud订阅捆绑包具有
科技
创意驱动增长,Adobe护城河够深吗?
Adobe通过其Creative Cloud订阅捆绑包具有
科技
-
 全力打造中国“创业之都”名片,第十届中国创业者大会将在郑州召开
北京创业科创科技中心主办的第十届中国创业
科技
全力打造中国“创业之都”名片,第十届中国创业者大会将在郑州召开
北京创业科创科技中心主办的第十届中国创业
科技
-
 智慧驱动 共创未来| 东芝硬盘创新数据存储技术
为期三天的第五届中国(昆明)南亚社会公共安
科技
智慧驱动 共创未来| 东芝硬盘创新数据存储技术
为期三天的第五届中国(昆明)南亚社会公共安
科技
-
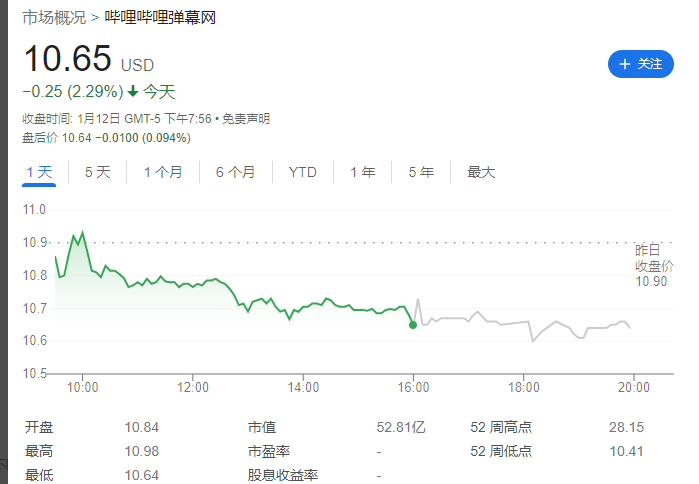 B站更新决策机构名单:共有 29 名掌权管理者,包括陈睿、徐逸、李旎、樊欣等人
1 月 15 日消息,据界面新闻,B站上周发布内部
科技
B站更新决策机构名单:共有 29 名掌权管理者,包括陈睿、徐逸、李旎、樊欣等人
1 月 15 日消息,据界面新闻,B站上周发布内部
科技
-
 苹果罕见大降价,华为的压力给到了?
1、苹果官网罕见大降价冲上热搜。原因是苹
科技
苹果罕见大降价,华为的压力给到了?
1、苹果官网罕见大降价冲上热搜。原因是苹
科技
-
 如何经营一家好企业,需要具备什么要素特点
我们大多数人刚开始创办一家企业都遇到经营
科技
如何经营一家好企业,需要具备什么要素特点
我们大多数人刚开始创办一家企业都遇到经营
科技
-
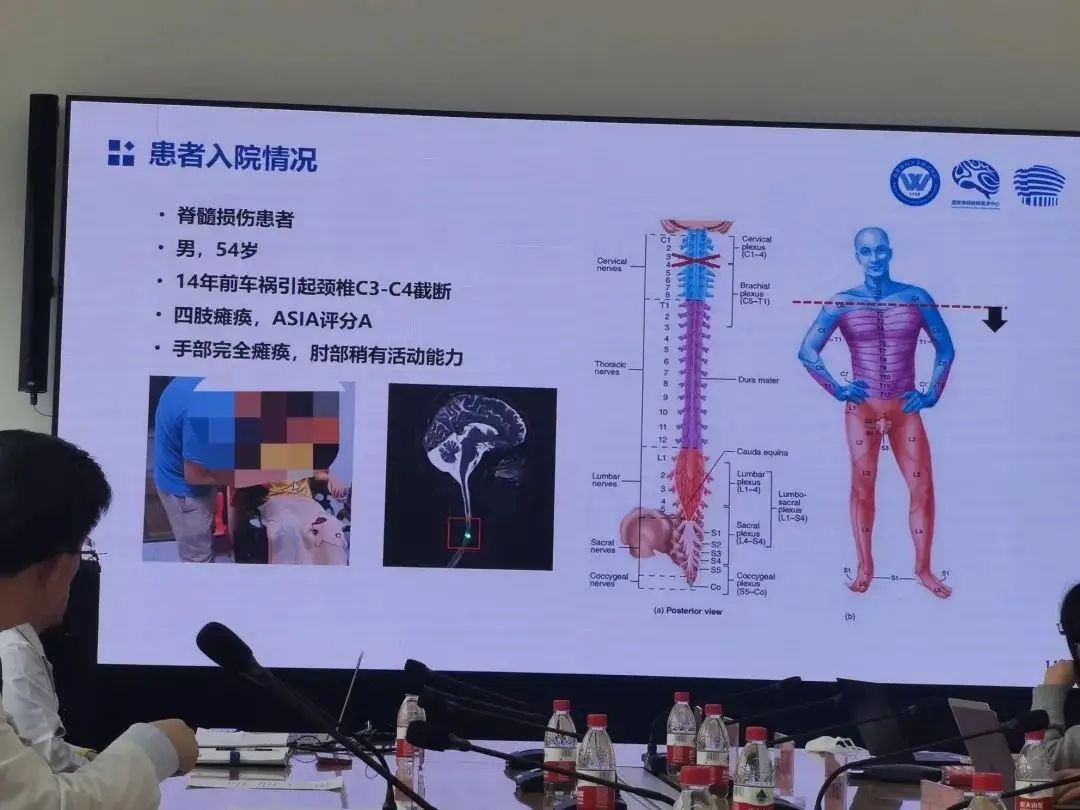 老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他由此产生了新的憧憬
瘫痪十四年后,老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他
科技
老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他由此产生了新的憧憬
瘫痪十四年后,老杨第一次再度抓握住一瓶水,他
科技
-
 丰田章男称未来依然需要内燃机 已经启动电动机新项目
尽管电动车在全球范围内持续崛起,但丰田章男
科技
丰田章男称未来依然需要内燃机 已经启动电动机新项目
尽管电动车在全球范围内持续崛起,但丰田章男
科技

